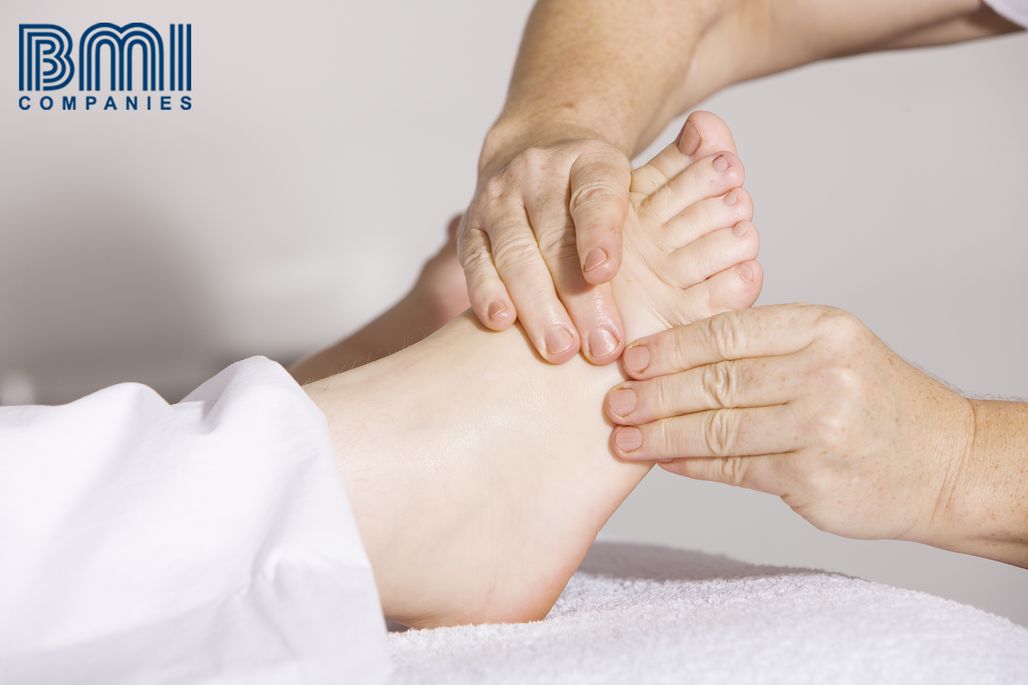
A very characteristic lesion of people with diabetes is the diabetic foot, which is the result of alterations in sensitivity. It is estimated that 15% of diabetics will present lesions compatible with a diabetic foot at some point in their lives.
The most important factors for its development are poor control of diabetes, neuropathy, foot deformities, arteriopathy and tobacco. These alterations facilitate the appearance of difficult-to-heal wounds that can become complicated.
The first signs that should alert are: an increase in the temperature of the foot, callused areas that do not improve, and that finally ulcerate. The strict control of diabetes and the rest of the risk factors mentioned above, notably reduces the incidence of these complications.
In this sense, some tips are:
• Do not cut the nails excessively
• Do not walk barefoot
• Check the water temperature before submerging your feet
• Use moisturizers
A frequent inspection by the doctor or nurses of the areas of the foot should be carried out, evaluating the sensitivity to detect the first signs of neuropathy.
Ocular complications associated with diabetes
Diabetes is associated with a group of eye problems that can lead to vision loss or even blindness. In particular, people with diabetes are at increased risk of:
• Diabetic retinopathy: which is damage to the retina, the innermost layer of the eye, caused by inadequate glucose control over a prolonged period.
• waterfallsCataracts are a darkening of the lens that blocks or changes the way light reaches the eye.
• Glaucoma: which is an increase in fluid pressure inside the eye that causes damage to the optic nerve and loss of vision. Diabetics have twice the risk of glaucoma than other people.
• Macular edema- A collection of fluid in the most sensitive area of the retina causing blurred vision in the central or lateral part of the visual field.
• Detached retina- One of the most common causes of blindness in diabetes, which occurs when blood vessels separate the retina from the back of the eye.
In addition to these possible problems, in diabetics, fluctuations in blood glucose levels cause refractive variations, which lead to increases or losses in visual acuity.
Cardiovascular complications associated with diabetes
Diabetes is a global problem that causes about 200,000 deaths per year in the world, associated with up to 80% of cases to cardiovascular causes. This disease is an independent risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke, and is closely related to high blood pressure, obesity, and hypercholesterolemia in metabolic syndrome.
Therefore, it is necessary to insist on strict control of diabetes, as well as not forgetting with the same conviction the control of the other factors that increase the risk of suffering from these diseases.